- +91-9484540774
- goodlifepainclinic@gmail.com
- Vadodara, Gujarat - 390015
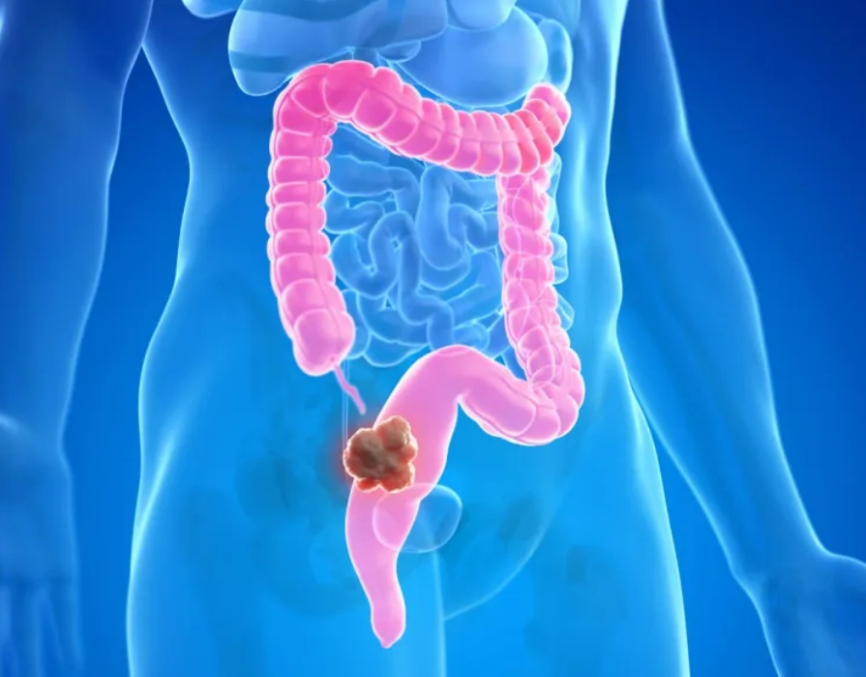
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is a type of cancer that starts in the colon or rectum. It is the third most common type of cancer in both men and women. Colon cancer starts as small, noncancerous clumps of cells called polyps, which can eventually turn into cancerous tumors if left untreated.
Precautions:
Get regular screenings: Starting at age 45 (or earlier if at high risk), schedule colonoscopies or other recommended screening tests.
Certain genetic syndromes: Mutations in certain genes can significantly increase risk
Initial Consultation: This starts with a detailed discussion of your medical history, including family history of colon cancer, personal history of polyps or inflammatory bowel diseases, and overall lifestyle habits. Symptoms like persistent changes in bowel habits, blood in stool, or unexplained weight loss are also crucial factors.
Physical Examination: Your doctor will perform a physical exam, paying attention to abdominal tenderness or masses. A digital rectal exam may also be conducted to check for abnormalities in the rectum and lower colon.
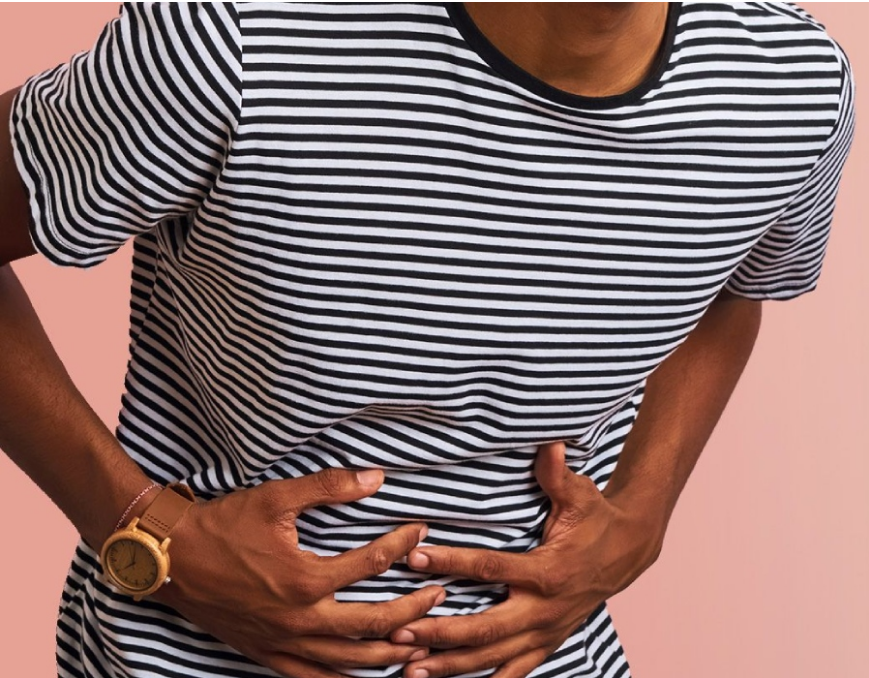

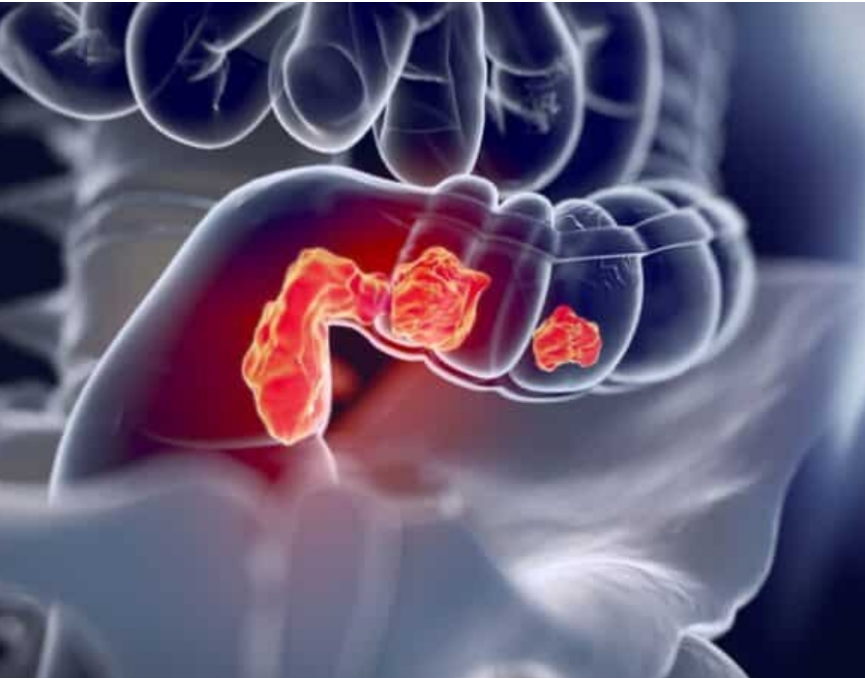
Colon cancer often develops silently, without causing any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, certain signs and symptoms may emerge, urging you to seek medical attention. Here are some key ones to be aware of:

Following your doctor’s orders is paramount. Strictly adhere to medication schedules, dietary restrictions, and activity limitations prescribed by your doctor, as these contribute significantly to successful treatment.
Managing side effects is crucial. Different treatments come with varying side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, pain, or bowel changes. Don’t hesitate to report any discomfort to your doctor so they can suggest effective management strategies,

Colon cancer treatment ends, but your journey continues. Here’s your 100-word guide to post-treatment support:

A: No guaranteed way, but healthy lifestyle (diet, exercise, weight control) reduces risk.
A: Family history increases risk, but most cases aren’t directly inherited. Genetic testing may advise further steps.
A: Depends on stage and type. Early detection improves cure chances. “Cured” means no evidence for several years.
A: May complement conventional treatment, but not replace it. Discuss with doctor for safety and effectiveness.
A: Many thrive after treatment. Adjustments may be needed, but support and healthy habits help you adapt and live well.
Cancer is on a rise. Each year more than 1 crore people lose their lives to cancer. We understand that the quality of life is equally important to the quantity of life. Our treatments always keep the quality of life in focus. This has helped us achieve exceptional patient outcomes.

Pain and Palliative Specialist
MBBS from KMC, Mangalore, Manipal University
MD Anaesthesia from People's College, Bhopal
FIAPM (Fellowship in Pain Medicine)
Daradia, Kolkata
EDPM - European Diploma in Pain Medicine, Belgium

Medical oncologist and Hematologist
MBBS from UCMS and GTB hospital, Delhi
MD Radiation oncology from the prestigious KGMU college, Lucknow
DM Medical Oncology from Ramiah Medical College/ HCG Ramiah Hospital, Bengaluru
ESMO - Certified European Society for Medical Oncology