- +91-9484540774
- goodlifepainclinic@gmail.com
- Vadodara, Gujarat - 390015
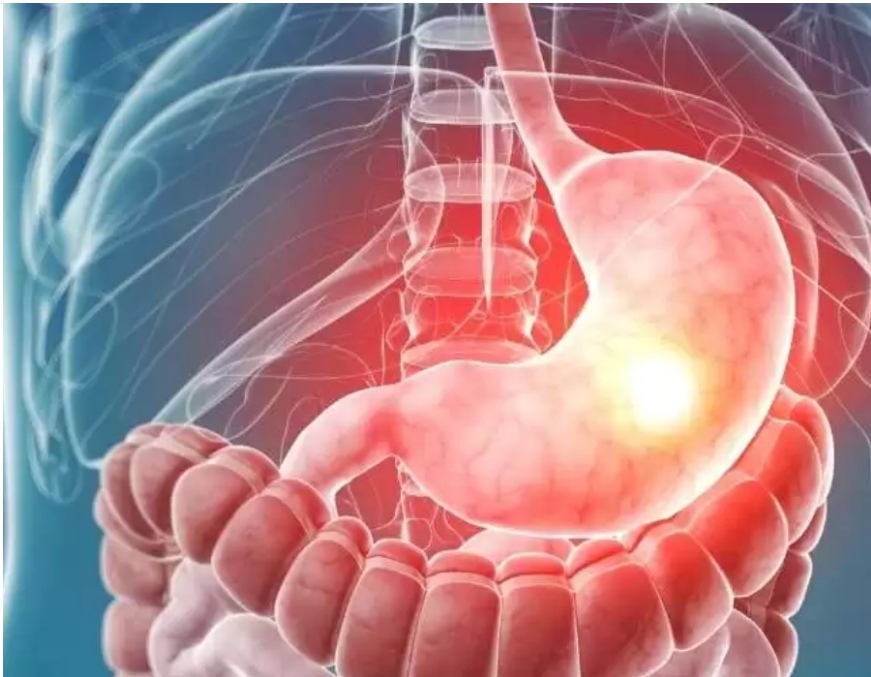
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a type of cancer that begins in the cells lining the stomach walls. It is the fifth most common cancer worldwide and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths. This type of cancer can be life-threatening if not detected and treated early. However, with awareness and early diagnosis, it is possible to beat stomach cancer and increase the chances of survival.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer, including age, gender, family history, and lifestyle habits. Individuals over the age of 50 are at a higher risk, and men are twice as likely to develop stomach cancer than women. Additionally, a family history of stomach cancer or certain genetic mutations can increase the risk.
Some lifestyle habits that may increase the risk include smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a diet high in salty, smoked, or pickled foods. Having a stomach infection caused by Helicobacter pylori bacteria, a history of stomach polyps or previous stomach surgeries, and obesity can also increase the chances of developing stomach cancer.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of stomach cancer, as early detection can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment. Some common symptoms include persistent stomach pain or discomfort, bloating, nausea, difficulty swallowing, and unintentional weight loss.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult your doctor for further assessment. They may perform a physical exam, order blood tests, or recommend imaging tests such as an endoscopy or CT scan to diagnose stomach cancer.
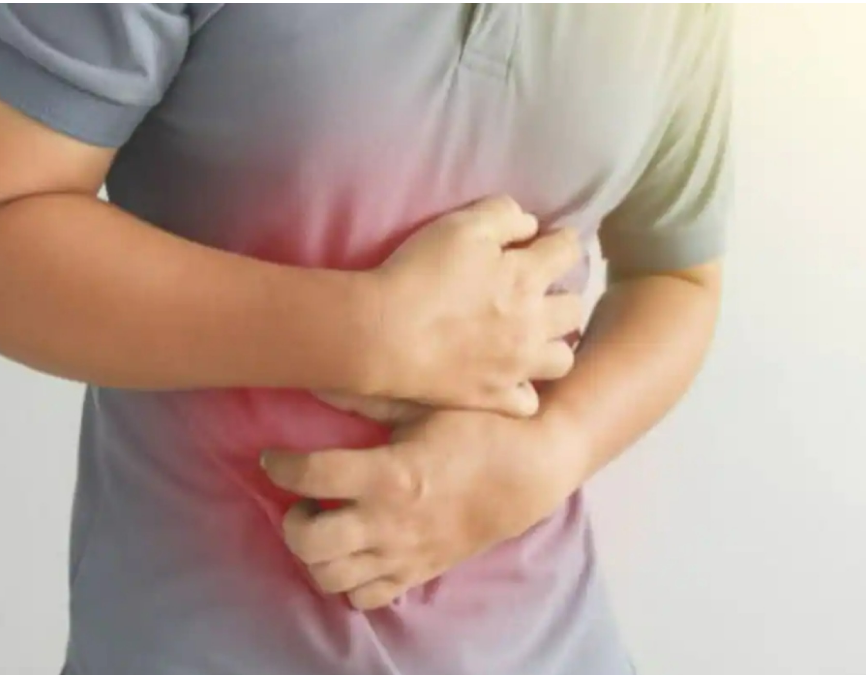
Stomach cancer can present with various signs and symptoms, which may vary depending on the location and stage of the cancer. Some early symptoms of stomach cancer include nausea, bloating, and stomach pain after eating. As the cancer progresses, individuals may experience a loss of appetite, difficulty swallowing, and unintentional weight loss.
In more advanced stages, stomach cancer may present with symptoms such as vomiting blood, black stools, and jaundice. It is important to note that these symptoms may also be indicative of other health conditions, so proper diagnosis is crucial.

Once a diagnosis of stomach cancer is confirmed, further evaluation is necessary to determine the stage and extent of the cancer. This may involve imaging tests such as CT scans, MRI, and PET scans, as well as biopsy to examine the tumor cells for characteristics.
These tests will help doctors develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs and stage of stomach cancer.

Treatment for stomach cancer may involve a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, Immunotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy. In some cases, a clinical trial may also be recommended. It is essential to follow all instructions provided by your healthcare team during treatment.
This may include following a specific diet to manage side effects, taking medications as prescribed, and attending all scheduled appointments. It is also important to communicate any concerns or issues that may arise during treatment with your healthcare team.

After completing treatment, it is crucial to attend follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor your recovery and check for any signs of cancer recurrence. It is also important to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to aid in your recovery.
Seeking support from family, friends, and support groups can be beneficial for emotional and mental well-being during this time. There are also various resources and programs available to assist with managing any lingering side effects and adjusting to life after stomach cancer.

A: There are steps you can take to reduce your risk, such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy diet and weight.
A: While a family history of stomach cancer may increase your risk, it does not necessarily mean you will develop the disease.
A: The chances of successful treatment and cure depend on various factors, such as the stage of cancer and individual health. Early detection and treatment increase the chances of survival.
A: There are no proven alternative therapies for stomach cancer. It is important to discuss any alternative treatments with your doctor before trying them, as they may interfere with your prescribed treatment plan.
A: Yes, with proper treatment and follow-up care, many people are able to resume their normal activities and lead fulfilling lives after stomach cancer treatment. It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and attend follow-up appointments for the best possible outcomes.
Cancer is on a rise. Each year more than 1 crore people lose their lives to cancer. We understand that the quality of life is equally important to the quantity of life. Our treatments always keep the quality of life in focus. This has helped us achieve exceptional patient outcomes.

Pain and Palliative Specialist
MBBS from KMC, Mangalore, Manipal University
MD Anaesthesia from People's College, Bhopal
FIAPM (Fellowship in Pain Medicine)
Daradia, Kolkata
EDPM - European Diploma in Pain Medicine, Belgium

Medical oncologist and Hematologist
MBBS from UCMS and GTB hospital, Delhi
MD Radiation oncology from the prestigious KGMU college, Lucknow
DM Medical Oncology from Ramiah Medical College/ HCG Ramiah Hospital, Bengaluru
ESMO - Certified European Society for Medical Oncology