- +91-9484540774
- goodlifepainclinic@gmail.com
- Vadodara, Gujarat - 390015

Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the cells of the breasts. It is the most common type of cancer among women and can also occur in men. Breast cancer can start in different parts of the breast, like the milk ducts or the lobules. It can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated.

Precautions:

Evaluating breast cancer goes beyond a simple yes/no answer. It requires thorough examination and professional judgment. While I can’t offer assessments, here’s what goes into it:
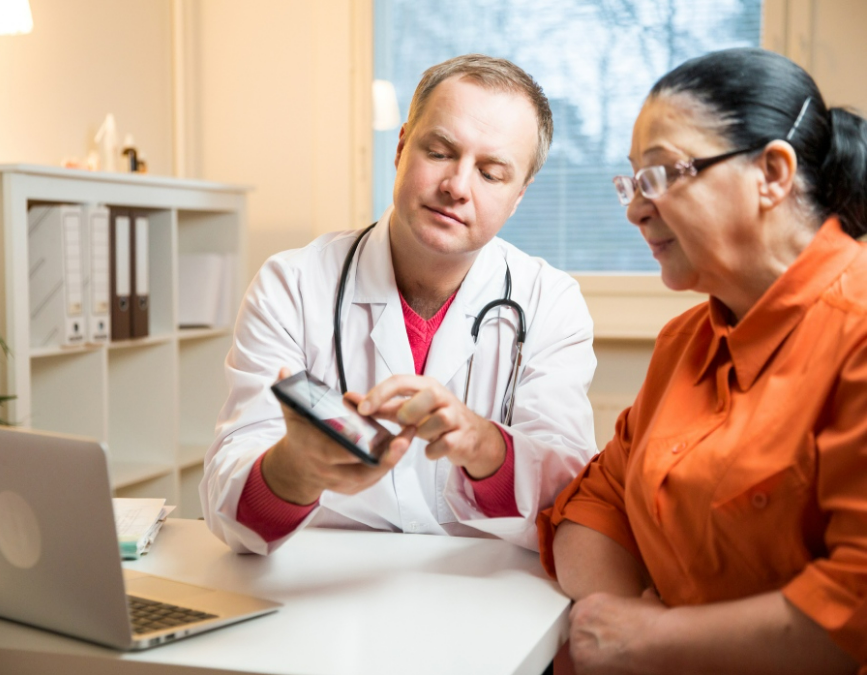

Once diagnosed, your doctor will recommend a treatment plan based on factors like type of cancer, stage, your overall health, and personal preferences. Some common treatment options include:


A: No guaranteed prevention, but healthy lifestyle (diet, exercise, weight control) can reduce risk.
A: Family history increases risk, but most cases aren’t directly inherited. Genetic testing may advise further steps.
A: Depends on stage and type. Early detection improves cure chances. “Cured” means no evidence for several years.
A: May complement conventional treatment, but not replace it. Discuss with doctor for safety and effectiveness.
A: Many thrive after treatment. Adjustments may be needed, but support and healthy habits help you adapt and live well.
Cancer is on a rise. Each year more than 1 crore people lose their lives to cancer. We understand that the quality of life is equally important to the quantity of life. Our treatments always keep the quality of life in focus. This has helped us achieve exceptional patient outcomes.

Pain and Palliative Specialist
MBBS from KMC, Mangalore, Manipal University
MD Anaesthesia from People's College, Bhopal
FIAPM (Fellowship in Pain Medicine)
Daradia, Kolkata
EDPM - European Diploma in Pain Medicine, Belgium

Medical oncologist and Hematologist
MBBS from UCMS and GTB hospital, Delhi
MD Radiation oncology from the prestigious KGMU college, Lucknow
DM Medical Oncology from Ramiah Medical College/ HCG Ramiah Hospital, Bengaluru
ESMO - Certified European Society for Medical Oncology